




The Republic of Tatarstan is leading among other regions of Russia in the implementation of the national project to create a comfortable urban environment. Currently, an eco-district is being created in Kazan. Various modern technologies are used here, including those that allow you to find out how you can benefit from seemingly completely unusable resources.
HPBS (Moscow), in a consortium with the Asadov Architectural Bureau, has proposed an interesting environmental solution for the efficient collection and use of rainwater. It is aimed not only at saving drinking water, but also at improving urban areas.
Composition of storm sewers
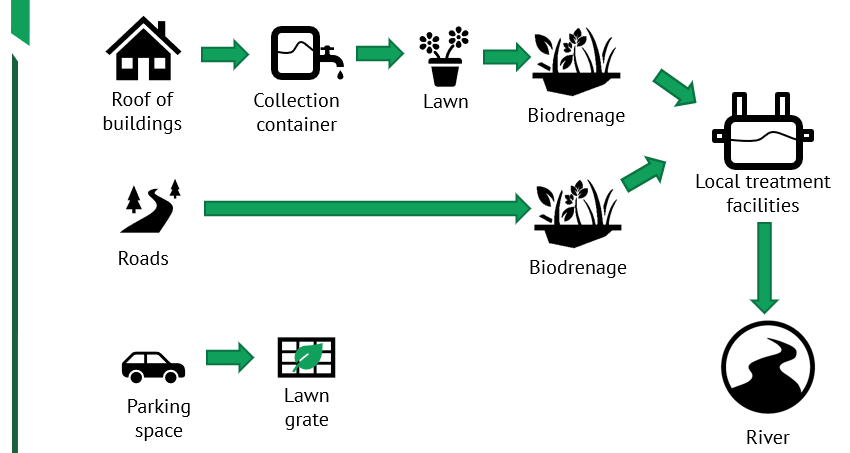
According to the project, rainwater flowing down drainpipes from the roofs of buildings gets into special tanks. They are located in the basements of houses or in the ground. The tanks must be ventilated and must be equipped with pre-filters for mechanical purification of water from dirt in the event that it is used for flushing in toilets. In addition, water can be used by residents for watering and washing the territory, technical use (for example, washing clothes, etc.).
As a rule, rainwater on the streets, due to blockages, and sometimes the absence of a storm sewer, collects in puddles that interfere with the passage of vehicles and pedestrians. An innovative approach has been developed to solve this problem. What is its essence?
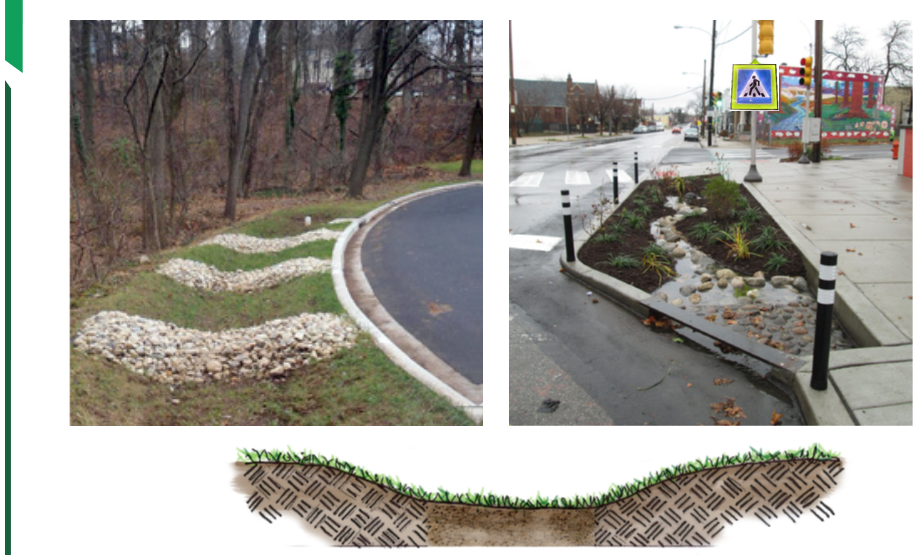
Water from roads and driveways flows into bio-drainage ditches (bioswales). Moisture-loving plants characteristic of a particular region are planted in them, which purify water. Gradually, it is absorbed into the ground or evaporates. If there is an excess of it (for example, when snow melts), water flows down bio-drainage ditches into specially equipped ponds or rain gardens. This approach allows you to naturally nourish plants, support life inside gardens.
Bio-drainage ditches

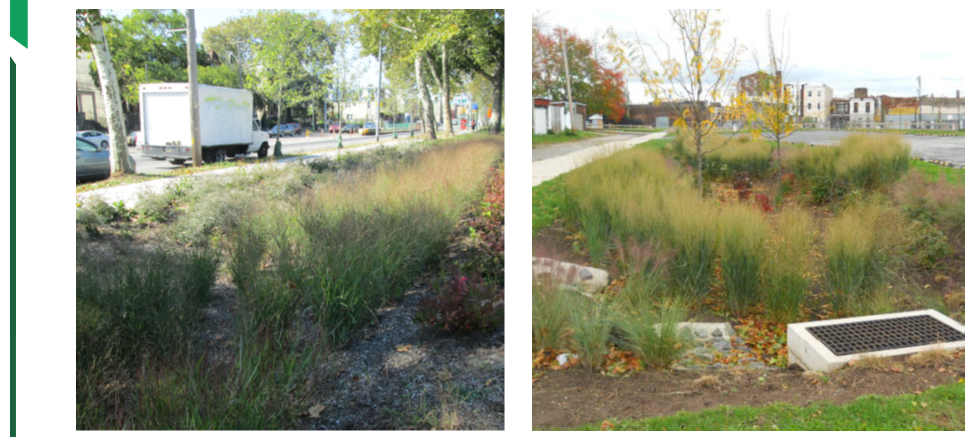
What are rain gardens? These are specially designated areas of natural vegetation, only more in-depth compared to the surrounding landscape. They are selected based on the analysis of height differences in this area. As mentioned above, rain runoff from biodrenage ditches is collected here. Rain gardens are also planted with local plants that are not afraid of periodic flooding and like a lot of moisture.
Rain Gardens

Decorative ponds are created on a similar principle. But unlike rain gardens, the bottom of ponds is covered with geomembrane – it does not allow water to soak into the ground. Rain gardens are adjacent to the pond, usually located at a higher elevation, so that the water remaining after soil enrichment flows into it.
There is an ecological component in all these decisions on the use of rainwater. Based on the use of “green” infrastructure, the authors of the project have developed the principle of operation of local wastewater treatment plants (VOCs). In this case, wastewater undergoes intensive biological treatment, disinfection and post-treatment of wastewater. The hydro-mechanical complex consists of artificial phytocards in a pond. It also has botanical grounds made of a filter layer of crushed stone of different fractions, arranged in rows. And already on their surface, a photo series is formed from plants such as cattails, reeds. The water is settled and discharged into the river already purified.
Rainwater collection system

The use of such “green” technologies contributes not only to the rational use of wastewater, but also to the improvement of the environment due to as many plants as possible, or the same rain gardens that will surely take root in other cities of Russia.