




The Sino-Singapore Tianjin Eco-City is being built 150 kilometers from the capital of China, Beijing, the result of joint cooperation between China and Singapore. The city being created implements the intentions of the two states to combat climate change, protect the environment and conserve resources. The first framework agreement on cooperation between states to create an Eco-City was signed back in November 2007.

The eco-city is located 45 kilometers from the city of Tianjin, which has a good transport network, including, in addition to several lines of express trains, a connection with the airport from which international flights are operated.
The area of the developed site is 30 km2, the planned population is 350,000 people. Prior to construction, the site was uninhabited, with deserted salt fields and ponds polluted by industrial emissions. By 2012, all 30 km2 had been cleared.
The spatial layout includes the main urban center, 2 sub-centers, 5 districts, a central green island with a reservoir inside, as well as water channels passing through the development area and access to the Bohai Bay (yellow sea).

The development of the city includes the organization of a national animation park (1 km2), a film and television park (1 km2), a science park (0.4 km2), an eco-information park (0.5 km2) and an eco-industrial park (1 km2), as well as many areas for leisure activities, including an amusement park.
Eco-city is a platform for innovation and implementation of new technologies in the field of ecology, energy conservation, emission reduction, green building economy and waste recycling. This is a national training center for working solutions in terms of environmental protection and a base for modern high-tech industries in the field of ecology, a working model of a socially harmonious and resource-saving society, an environment for international cooperation in terms of development and implementation of ideas for protecting and preserving the environment.
The development of the Eco-city indicator system was carried out with the involvement of international experts. The system consists of four qualitative and 22 quantitative categories, which are further broken down into 51 key factors and 129 key components, 275 targets and 723 measures to monitor the implementation of implemented solutions.
The examples of indicators:
1. Economy:
2. Ecology and environment:
3. Resources:
4. Society:
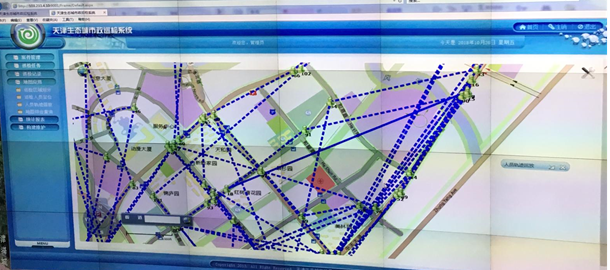
Today (October 2018), more than 100 thousand people already live in the city. The functioning and monitoring of city systems is carried out according to the principles of a smart city. The city has an information center that allows monitoring of all processes in near real time, for example, determining the amount of energy and water consumed by buildings and urban infrastructure, energy generated by wind turbines, solar systems and solar power plants. The monitoring system makes it possible to identify the problem and its source (for example, water leaks) in time. All information is kept for 25 years.
All residents have access to city services and community centers at a distance of no more than 500 m.

The share of energy generated from renewable sources is 20%.

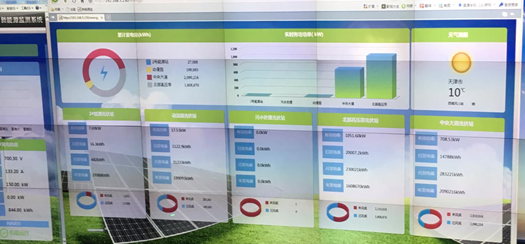
More than 50% of the water consumed is locally treated water. More than 70% of the plants in the city are native plants that do not require special care.

All completed buildings are certified by the China Green Building Certification System, and about 20% of them have the highest certification rating (3 stars).

The city has a vacuum waste disposal system. All 100% of waste is cleaned from harmful / hazardous content, more than 60% of waste is recycled.

Nearly half of the trips made in the city are organized by non-conventional fuel vehicles, a figure set to reach 90% by 2020. The transport infrastructure has been developed in accordance with the principles of a smart city. The length of the pedestrian paths is already well over 50 km, while the total length of the pedestrian paths planned by the time the development of the city is completed is 100 km.
Job balance index – above 50%.
More than 6 thousand companies are registered in the city. There is no classical production in the city, but high-tech enterprises in the field of low-carbon production, recycling technologies are developing, large companies are buying and renting offices.
Development of an Integrated Energy Supply and Energy Efficiency Strategy
https://hpb-s.com/en/services/the-concept-of-using-alternative-and-renewable-energy-sources/